Quick links to procedures on this page:
Creating image maps
An image map is a single graphic with clickable areas, or hotspots, that link to Web pages. A hotspot is defined using co-ordinates on an image, and an URL is assigned to each defined area.
If you want to add rollovers to an image, or to assign different file formats or compression rates to parts of an image, you can slice it instead of creating an image map. For information about creating sliced images, see “Slicing images.”
Creating clickable areas
Hotspots are created from objects. You can assign an URL and alternative text to an object. You must also specify the shape for a hotspot; it can be a polygon that closely follows an object’s shape, a rectangle that matches an object’s highlighting box, or a circle that encloses an object.
If you want to create an image map using a photo, you can define an editable area where you want a hotspot to be, and then convert the editable area into an object.
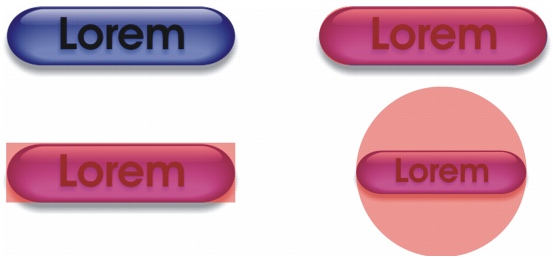
The hotspot on the left button is rectangular, while the hotspot on the right button is circular. Clicking anywhere on the hotspot activates it.
Exporting image maps
When you export an image map, you must choose one of three different map types: client-side, server-side, or client/server-side. The client-side image map type is most common and is the default setting. The following files are generated automatically, depending on the image map type you choose:
|
•
|
|
an HTML page for client/server-side, client/server-side, and client-side image map types.
|
To create a clickable area for an image map |
|
1.
|
|
In the Objects docker, right-click an object’s thumbnail, and select Properties.
|
To export an image map |
|
6.
|
|
In the next dialog box, specify the options associated with the selected file format, and click OK.
|
|
7.
|
|
In the Save map file dialog box, choose one of the following map types from the Save as type list box:
|
|
•
|
Client-side (*.htm) — specifies that your image map does not depend on a server to process map information. This is the default and is the most common setting.
|
|
•
|
Client/Server-side NCSA — creates the files required for both client and NCSA server sides
|
|
•
|
Client/Server-side CERN — creates the files required for both client and CERN server sides
|
|
If you are saving a client-server or server-side image map, type a name for the map file in the Map name box.
|
![]()
|
•
|
|
You must save your image to a Web-compatible file format, such as GIF or JPEG. For information about choosing a file format, see “Choosing a Web-compatible file format.”
|
![]()
|
•
|
|
You can also define hotspot areas for an image map using the Internet toolbar. Click Web
|